- When extra NH3 is added to the following system at equilibrium:3 H2(g) + N2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When N2 is removed from the following system at equilibrium:3 H2(g) + N2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When H2 is added to the following system at equilibrium:3 H2(g) + N2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When the pressure is increased on the following system at equilibrium:3 H2(g) + N2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When the pressure is decreased on the following system at equilibrium:3 H2(g) + N2(g) ⇌ 2 NH3(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When the temperature is decreased on the following system at equilibrium:2 HCl(aq) + Mg(s) ⇌ MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) + heat
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When the temperature is increased on the following system at equilibrium:2 HCl(aq) + Mg(s) ⇌ MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) + heat
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
- When the temperature is decreased on the following system at equilibrium:2 HCl(aq) + Mg(s) ⇌ MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) + heat
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts right, toward products
- In order to restore equilibrium, the reaction shifts left, toward reactants
- No change occurs
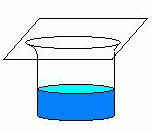
The system depicted here is maintained at a temperature of 30 degrees celsius. If the temperature of the system is doubled, the system will achieve equilibrium by which of the following responses?- A higher percentage of the water vapor in the container will condense to liquid.
- A higher percentage of the water will move into the vapor phase.
- The temperature of the liquid water will exceed the temperature of the vapor.
- The temperature of the vapor will exceed the temperature of the liquid water.
- When the temperature is increased on a closed system containing water and its vapor at equilibrium:H2O(l) + heat ⇌ H2O(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, more liquid water evaporates
- In order to restore equilibrium, water vapor condenses to form liquid water
- No change occurs
- When the temperature is decreased on a closed system containing water and its vapor at equilibrium:H2O(l) + heat ⇌ H2O(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, more liquid water evaporates
- In order to restore equilibrium, water vapor condenses to form liquid water
- No change occurs
- When the pressure is decreased on a closed system containing water and its vapor at equilibrium:H2O(l) + heat ⇌ H2O(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, more liquid water evaporates
- In order to restore equilibrium, water vapor condenses to form liquid water
- No change occurs
- When the pressure is increased on a closed system containing water and its vapor at equilibrium:H2O(l) + heat ⇌ H2O(g)
- In order to restore equilibrium, more liquid water evaporates
- In order to restore equilibrium, water vapor condenses to form liquid water
- No change occurs
- The process of dissolving Na2SO4 in water is known to be exothermic:Na2SO4(s) ⇌ 2 Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + heat
If the temperature of the solution is decreased, Na2SO4 becomes:- More soluble
- Less soluble
- No change in solubility occurs
- The process of dissolving Na2SO4 in water is known to be exothermic:Na2SO4(s) ⇌ 2 Na+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + heat
As the temperature of the solution increases, Na2SO4 becomes:- More soluble
- Less soluble
- No change in solubility occurs
- This is the aqueous iron(III) thiocyanate equilibrium:Fe3+(yellow) + SCN-(colorless) ⇌ [FeSCN]2+(dark red)
If aqueous iron(III) chloride is added to the solution at equilibrium:- The solution becomes colorless
- The solution becomes more yellow
- The solution turns darker red
- No change in color occurs
- This is the aqueous iron(III) thiocyanate equilibrium:Fe3+(yellow) + SCN-(colorless) ⇌ [FeSCN]2+(dark red)
If aqueous potassium thiocyanate is added to the solution at equilibrium:- The solution becomes colorless
- The solution becomes more yellow
- The solution turns darker red
- No change in color occurs
- A beaker with a mixture of ice and water is maintained at equilibrium:H2O(s) + heat ⇌ H2O(l)
If the temperature of the system is increased:- Ice melts to form liquid water (shift to the right)
- Water freezes to form ice (shift to the left)
- No change occurs
- A beaker with a mixture of ice and water is maintained at equilibrium:H2O(s) + heat ⇌ H2O(l)
If the temperature of the system is decreased:- Ice melts to form liquid water (shift to the right)
- Water freezes to form ice (shift to the left)
- No change occurs
- A precipitation reaction achieves equilibrium:BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) ⇌ 2 NaCl(aq) + BaSO4(s)
If barium chloride (BaCl2) is added to the system, which change occurs?- The reaction shifts to the right, and more precipitate is produced
- The reaction shifts to the left, and some precipitate dissolves
- No change occurs