- If an atom of polonium (atomic number 84) undergoes a conversion to lead (atomic number 82) by the loss of a single particle,
- the particle lost was a positron
- the particle lost was an alpha particle
- the particle lost was a gamma ray
- the particle lost was a beta particle
- the particle lost could have been an alpha particle or a beta particle
- Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are stable isotopes of the element. Which of the following isotopes of carbon is likely to undergo positron emission?
- carbon-11
- carbon-12
- carbon-13
- carbon-14
- carbon-15
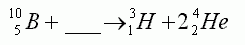
In the equation shown here, the missing particle is:-
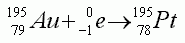
- The equation shows an example of beta particle decay
- The equation shows an example of positron emission
- The equation shows an example of alpha particle emission
- The equation shows an example of electron capture
- The equation shows an example of gamma ray emission
- Bones found in the Lascaux Caves in France have a carbon-14 disintegration rate of 2.25 disintegrations per minute per gram of carbon. If the rate of decay rate of carbon-14 at the time of death is 13.6 counts per minute per gram of carbon, calculate the age of the remnants. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years.
- 7.5 x 104 years
- 1.91 x 102 years
- 8.2 x 106 years
- 1.5 x 104 years
- 2.3 x 103 years
- After polonium-214 undergoes an alpha decay and two beta decays, the particle produced is:
- lead-206
- polonium-210
- radon-222
- bismuth-214
- lead-214
- Phosphorus-15 has a half-life of 14 days. What proportion of the original phosphorus-15 remains after 8 weeks?
- 1/2
- 1/4
- 1/8
- 1/16
- 1/32
- The decay rate constant for a newly discovered element, tentatively named "Allanium", is 2.4 x 10-2 s-1. What is the half-life of the new element.
- 29 s
- 0.017 s
- 0.035
- 1.2 years
- 7.2 s
- The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. If a sample of wood is found to have only 13.2% of its original carbon-14 remaining, how old is the piece of wood?
- 2.13 x 104 years
- 4.35 x 105 years
- 7.11 x 104 years
- 1.67 x 104 years
- 9.00 x 10-3 years
- The number of radioactive nuclides in a sample decays from 9.34 x 1023 to 5.42 x 1023 in 28 minutes. What is the half-life of the nuclide?
- 35.7 minutes
- 23.1 minutes
- 30.1 minutes
- 2.45 x 103 minutes
- 24.4 minutes-1
- One fission process of uranium-235 is:
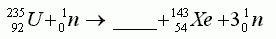
What is the missing particle? -
- Electron capture would transform carbon-12 into what nuclide?
- boron-13
- boron-12
- carbon-13
- nitrogen-13
- carbon-11
- The nuclide radium-226 is the daughter nuclide resulting from the a decay of what parent nuclide?
- radon-222
- thorium-228
- thorium-230
- polonium-214
- radium-225
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:23992U + 42He → _____ + 10n
- 24194Pu
- 24394Pu
- 24392U
- 24192U
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:2713Al + 42He → 3015P + _____
- 10n
- 11H
- 6130Zn
- 74Be
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:24195Am + 42He → 210n + _____
- 24397Bk
- 23697Bk
- 24393Np
- 24493Np
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:21484Po + 242He + 20-1e → _____
- 22286Rn
- 21888Ra
- 22284Po
- 21886Rn
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:2713Al + _____ → 2411Na + 42He
- 10n
- 10H
- 0-1e
- 2813Al
- Identify the missing coefficient in the following nuclear reaction:23592U + 10n → ____10n + 13956Ba + 9436Kr
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:3719K → _____ + 0+1e
- 3718Ar
- 3720Ca
- 3818Ar
- 3618Ar
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:11H + 31H → _____
- 42He
- 20n
- 42Be
- 31H
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:94Be + 11H → _____ + 42He
- 63Li
- 147N
- 52He
- 41H
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:_____ → 42He + 20881Tl
- 21283Bi
- 20479Au
- 20483Bi
- 21279Au
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:23994Pu → 42He + _____
- 23592U
- 24396Cm
- 23596Cm
- 24392U
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:______ + 10n → 14256Ba +9136Kr + 310n
- 23592U
- 23795Am
- 23392U
- 23792U
- Identify the missing coefficient in the following nuclear reaction:23592U + 10n → ____10n + 13953I + 9539Y
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:63Li + 10n → 0-1e + 42He + _____
- 32He
- 21H
- 114Be
- 115B
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:4219K → 0-1e + _____
- 4220Ca
- 4218Ar
- 4119K
- 4120Ca
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:22688Ra → 42He + _____
- 22286Rn
- 23090Th
- 22290Th
- 23086Rn
- Identify the missing particle in the following nuclear reaction:9943Tc → _____ + 0-1e
- 9944Ru
- 9943Tc
- 9942Mo
- 9943Es
- A process in which a very heavy nucleus splits into more-stable nuclei of intermediate mass is called:
- nuclear fusion
- nuclear fission
- radioactive decay
- a chain reaction
- radiocarbon dating
- Which of the following statements is true?
- All man-made isotopes are radioactive
- Some man-made isotopes are radioactive
- None of the man-made isotopes are radioactive
- Which of the following statements is true?
- All naturally occurring isotopes are radioactive
- Some naturally occurring isotopes are radioactive
- No naturally occurring isotopes are radioactive
- An electron emitted from the nucleus during some kinds of radioactive decay is known as:
- An alpha (a) particle
- A beta (b) particle
- A positron
- A gamma ray
- An alpha (a) particle is essentially a ____________________ nucleus.
- hydrogen
- uranium
- carbon-12
- helium
- plutonium
- Gamma (g) rays are:
- are very high energy, very short wavelength electromagnetic radiation
- are very high energy, very long wavelength electromagnetic radiation
- are very low energy, very short wavelength electromagnetic radiation
- are very low energy, very long wavelength electromagnetic radiation
- Very large nuclei tend to be unstable because of the:
- repulsive forces between electrons
- attraction of electrons for the positively charged nucleus
- repulsive forces between neutrons
- repulsive forces between protons
- attraction of protons for neutrons
- For the most common types of radioactive decay, the order of mass from lightest to heaviest is:
- gamma, alpha, beta
- beta, alpha, gamma
- beta, gamma, alpha
- gamma, beta, alpha
- For the most common types of radioactive decay, the order of least penetrating to human tissue, to most penetrating to human tissue is:
- gamma, alpha, beta
- alpha, beta, gamma
- beta, gamma, alpha
- gamma, beta, alpha
- For the most common types of radioactive decay, the order of least dangerous to most dangerous is:
- gamma, alpha, beta
- alpha, beta, gamma
- beta, gamma, alpha
- gamma, beta, alpha
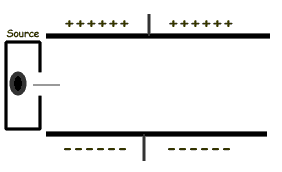
Assuming that the radiation source above emits gamma rays, as the rays pass between the charged plates they will:- pass straight through
- be deflected downward
- be deflected upward

Assuming that the radiation source above emits alpha particles, as the particles pass between the charged plates they will:- pass straight through
- be deflected downward
- be deflected upward

Assuming that the radiation source above emits beta particles, as the particles pass between the charged plates they will:- pass straight through
- be deflected downward
- be deflected upward
- In nuclear reactions:
- small amount of mass are converted to large amounts of mass
- large amount of energy are converted to small amount of mass
- small amounts of mass are converted to large amount of energy
- mass and energy are destroyed
- Compared to chemical reactions, nuclear reactions produce:
- proportionally far less energy
- proportionally far more energy
- fewer changes in the nucleus
- more vegetables